What Are Translations and Translation Keys?
A significant aspect of internationalization is that messages or texts within the HMI are automatically translated into the language selected by the current user.
In HELIO, a
Translationis used to convert user-facing texts and messages into different languages. ATranslationincludes a version for each of the supported languages.A translation is uniquely identified in a HELIO Runtime using its
TranslationKey. This key is the unique identifier of this translation.
How Do I Define Translations in HELIO?
There are two approaches to define translations in HELIO: implicitly and explicitly. Each method has its advantages and is typically used by different people or at different times:
Approach | How? | Used When? | Used By? |
|---|---|---|---|
Implicitly | Translations are created while you add new Elements to your HMI. Whenever you edit a property of the type Localizable Text (Dynamic Property) and save your project this text will get stored in the Translation Database of HELIO. | Throughout the project. | HMI Engineers UX Specialists |
Explicitly | Translations are created while you add new Elements to your HMI. Whenever you edit a property of the type Localizable Text (Dynamic Property) and save your project this text will get stored in the Translation Database of HELIO. | Typically when the HMI is finalized towards the end of a project. | Technical Editor Translator |
Implicitly
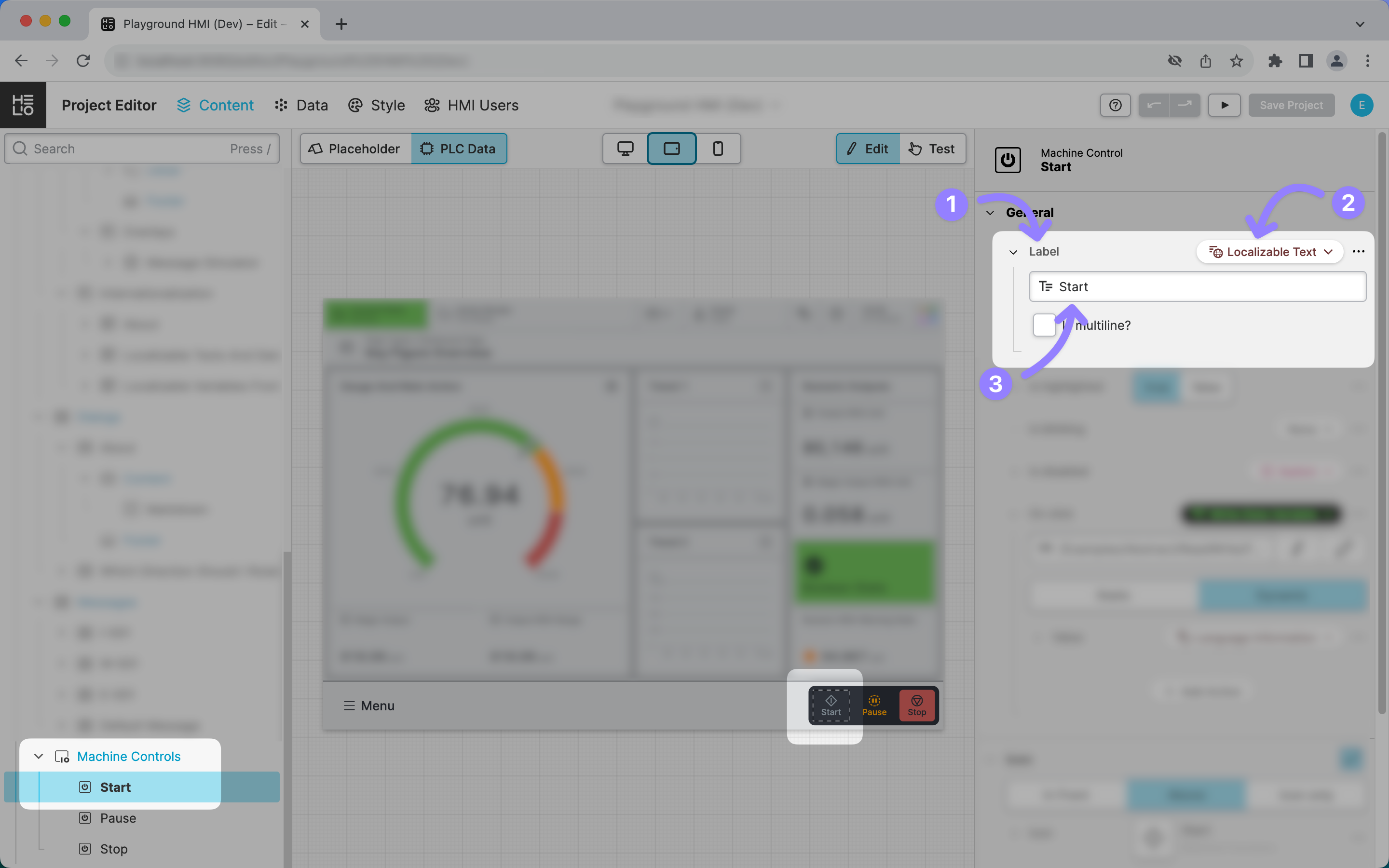
Translations can be defined in the context of a project within the Content View.
- The
LabelProperty of thisMachine Controlshould be translated. - That’s why it uses the property type Localizable Text (Dynamic Property).
- The value of this property defines the
TranslationKey, which, in this case, is the translation in the default language, English. However, you could also opt to use a unique key that more stable, won’t change over time, but still communicates its text's purpose .e.g.MainFunctions.Start.Label.
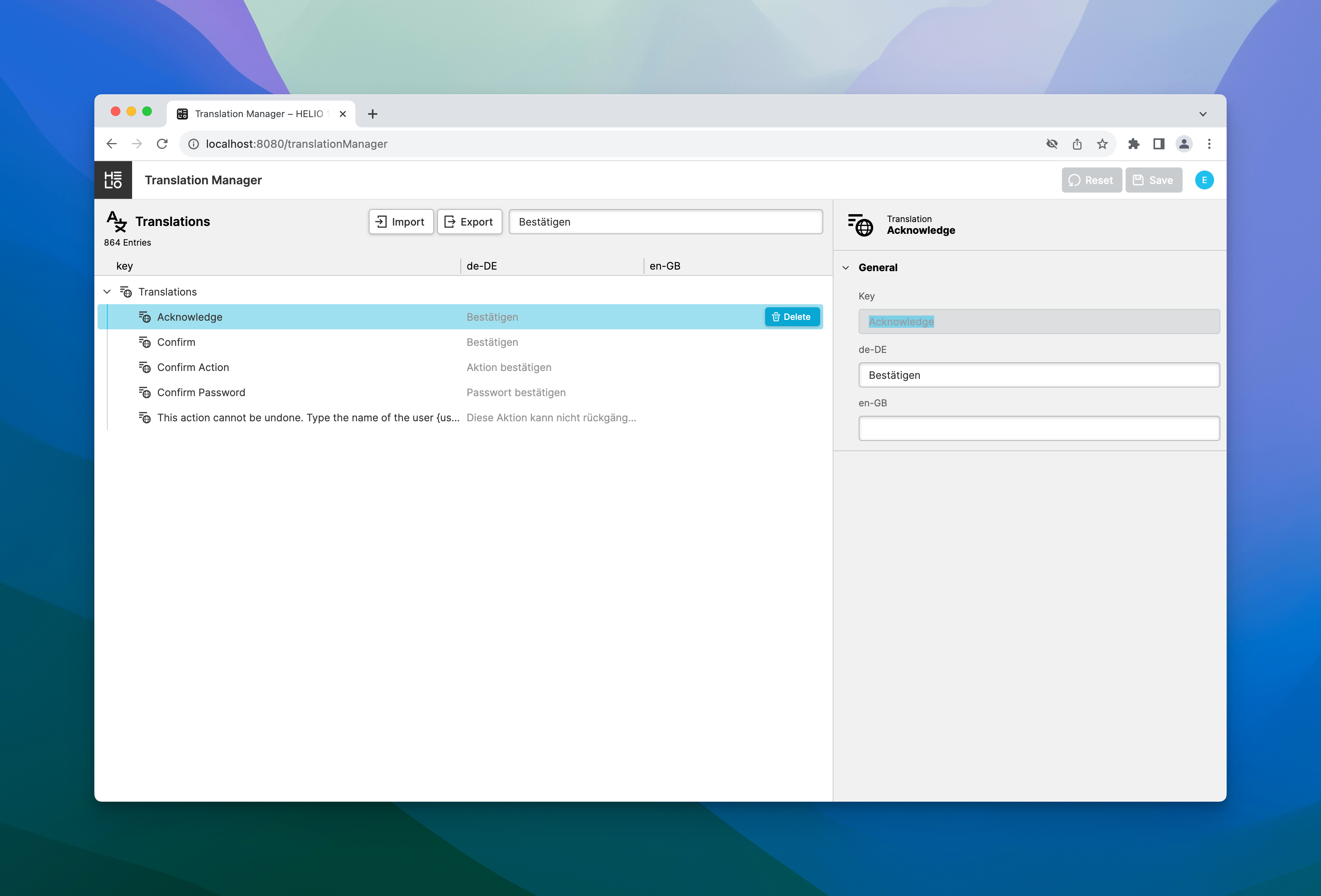
Explicitly
Translations can be defined across projects in a central location:
Learn more with the following resources: