Condition (Dynamic Property)
About
Use a Condition to solve more complexe rules by comparing the
two values (the Left Operand and the Right Operand).
For example you might display a helpful hint when a Data Variable (Dynamic Property) fallse below a certain threshold.
Anatomy
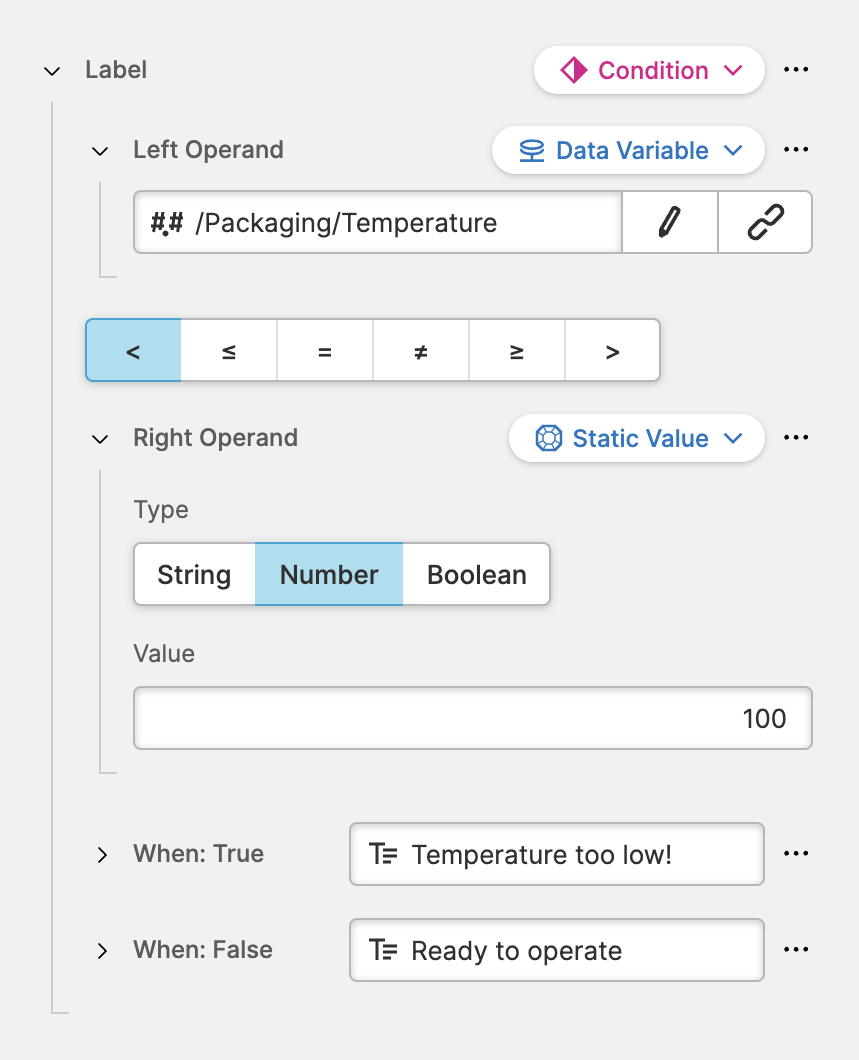
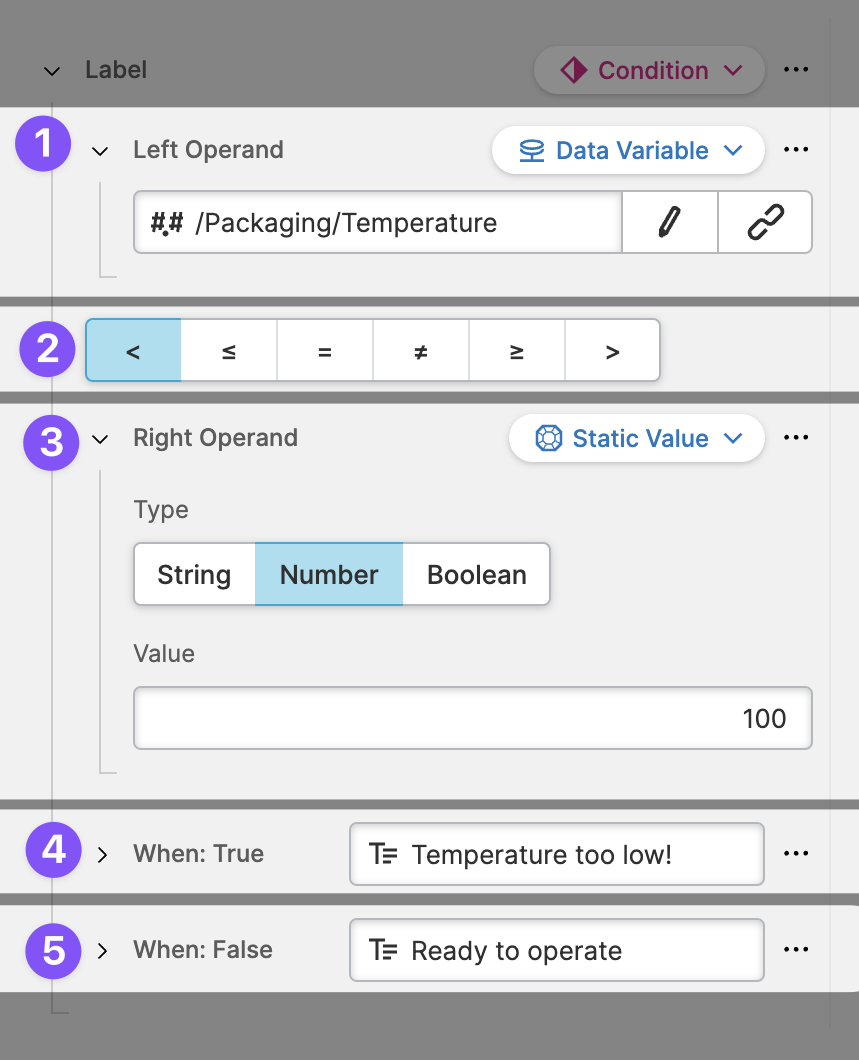
Left Operand
This is the value you want to compare. It is a Dynamic Property, so feel free to compare any type you like. In most of the cases you'll propably use a Data Variable (Dynamic Property).Comparison Operator
Describes how the two values will be compared. This will adjust to the type of the variables you compare. In this example we're seeing operators to compare numerical values (less than, less then or equal, …).Right Operand
This is the value with which you want to make a comparison. Any yes, it is also a Dynamic Property, so let your imagination run wild.When: True
If the comparison turns out to be truthy this value will be used as the actual value. By default, the value istrue. However, as this property is dynamic, you can use any type you prefer, such as a Data Variable (Dynamic Property) or a Localizable Text (Dynamic Property).When: False
If the comparison turns out to be falsy this value will be used as the actual value. By default, the value isfalse. Again, you can also use any Dynamic Property that works for you.
Examples
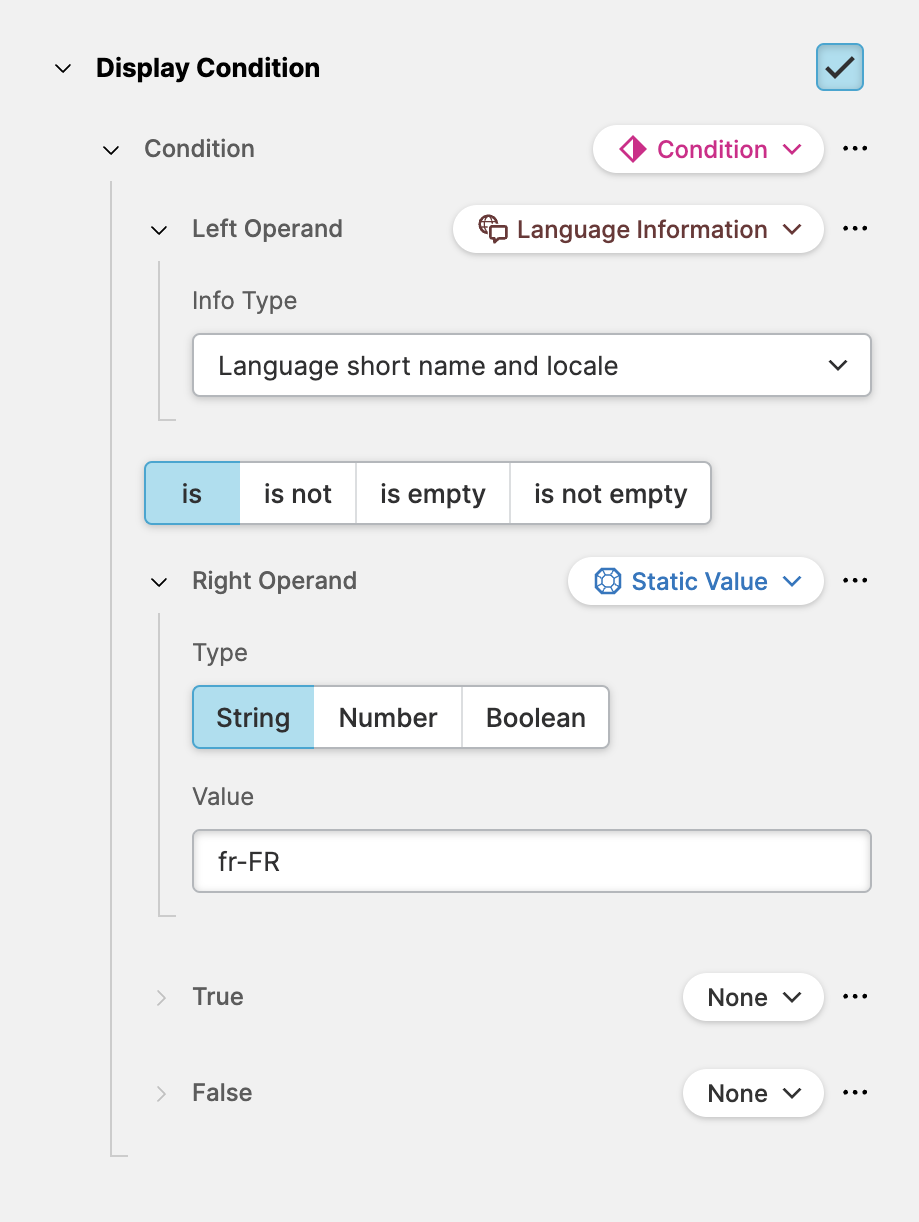
Reacting to a Specific Language
In this example the Language Information type has been chosen as the Left
Operand. Since it returns a String the Comparison Operator switched to
operators that work with text content.
The condition is applied to the Display Condition which means that we should make sure to set it to a boolean value. In such a situation can simply apply the default values for the falsy and truthy case.